Theme: Exploring new pathways through discoveries in making Liver healthy
Liver Congress 2018
- About 3rd World Liver Congress
- Sessions/Tracks of Liver Congress 2018
- Market Analysis Report of Liver Congress 2018
- New Updates- Liver Congress 2018
- Past Conference Report
Liver Congress 2018
ME Conferences takes a lot of privilege to invite all the scholars and researchers from all over the world to expatiate about their respective scientific research at “3rd World Liver Congress” which is CPE accredited. An opportunity to experience this grand colloquium along with the most alluring city Abu Dhabi, UAE on December 17-18, 2018 .and theme of the conference is “Exploring new pathways through discoveries in making Liver healthy”. Liver Congress 2018 is a unique platform for a focused plan of the current research in the field of Hepatology which includes prompt Keynote presentations, Oral talks, Poster presentations, Delegate views, board talks, and Exhibitions. We invite Gastroenterologists, Hepatologists, Cardiologists, Neurologists, Nephrologists, General Physicians, Microbiologists, Virologists, Pathologists, Oncologists, Surgeons and Toxicologists, Researchers, Students, Business delegates and Young researchers across the globe.
Why attend?
It is a worldwide platform for people around the world to discuss liver and liver-related diseases, this is best opportunity to accomplish the greatest gathering of participants from around the world to conduct presentations, distribute and update knowledge. This Liver Congress 2018 will coordinate, disperse information and meet with recurring pattern and potential investigators and get name affirmation at this 2-day event. Broadly World-eminent speakers and researchers with the most recent frameworks, methodologies, and the most current updates in the field of the liver in connection with various branch of medicine, are indications of this conference. This International Conference on the liver or rather all Liver and Hepatology gatherings, Liver events and liver Congress will help in specialists, academicians, and frameworks organization.
Target Audience
-
Deans and Professors of medicine and Hepatology departments
-
General Physicians
-
Doctors
-
Business Professionals
-
Medical Colleges
-
Scientists and Researchers organizers
-
Research Scholar
-
Consultants
-
Lab Technicians
-
Healthcare professionals
-
Founders and Employees of the related companies
-
Clinical investigators & Researcher
-
Hospitals and Health Services
-
Pharmaceutical companies
-
Nurse and nursing education institutions
Highlights of Latest Advances on Liver Congress 2018
Track 1: Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Gastroenterology is the branch of medicine with deals with the digestive system and its disorders. Gastroenterology deals with the diseases affecting the gastrointestinal tract, and its related organs starting from the mouth to the anus. Hepatology is also the branch of medicine with deals with the study of gallbladder, liver, pancreas and biliary tree and as well as their disorders. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and hepatology allow us to investigate biology from the atomic level to the community level. Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology elements the most recent discoveries with respect to the liver structure and function other organs from the atomic level to organ level.
Track 2: Liver Inflammation and Immunology
The human liver is perceived as a non-immunological organ which primarily engaged in metabolic, nutrient storage and detoxification activities but it has many unique immunological properties, including induction of immune tolerance, strong innate immunity, poor adaptive immune response versus over-reactive autoimmunity and hematopoiesis in the fetal liver. The healthy liver is a site for immunological activity with a diverse immune cell repertoire as well as non-hematopoietic cell populations. The innate immunity like hepatocytes provides protection against hepatic and systematic bacterial infections. Kupffer cells, also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer-Browicz cells are specialized macrophages located in the liver, lining the walls of the sinusoids that form part of the mononuclear phagocyte system.
-
Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency
-
Drugs or toxins
-
Wilson’s disease and related disorders
-
Bacterial Infection
-
Bile Duct Obstruction
-
Protozoan Infection
-
Hepatotoxicity
Track 3: Liver Regeneration
The liver is a visceral organ which has a unique power of regeneration, this property is called homeostasis, in spite of surgically removed the liver can grow back to a full size. Liver regeneration involves the regeneration of liver cells like hepatocytes which possess an unlimited capacity for proliferation, sinusoidal endothelial cells, and biliary epithelial cells. It is a highly controlled process regulated on highly redundant signals by complex pathways and these signaling pathways are known to stimulate by growth factors, hormones, cytokines, and nuclear receptors but the excess accumulation of fats may interfere with the regeneration mechanism of the hepatocytes.
-
The clonogenic capacity of hepatocytes
-
Proliferation and differentiation
-
Hepatocyte growth factor
-
Other factors
Track 4: Gene Expression in Liver
There is a higher genetic diversity in tumor cells which holds at the gene expression level. Through knowing the gene expression level we can regulate the hepatocellular carcinoma during hepatitis viral infection. Disease progression in HBV and HCV induced can influence by both environmental factors and genetic risk factors. Nucleic acid-mediated gene therapy has been undergoing clinical trials which may result towards prevention of chronic liver diseases by regulating mechanism of different proteins expression using miRNA overexpression and miRNA functional silencing.
-
Genetics and epigenetics of liver cancer
-
Human liver proteome project
Track 5: Hepato-nephrology
Hepato-nephrology is the field that deals with how the liver disease is affecting the kidney function. Hepatorenal syndrome is the medical condition that occurs in patients suffering from fulminant liver failure, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis which results in rapid deterioration of kidney function with an infection, bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract or overuse of diuretics. Patients show other symptoms like jaundice, altered mental status, evidence of decreased nutrition, the presence of ascites and elevated pressures in the portal vein system, elevated pressures in the portal vein system.
-
Trichohepatoenteric syndrome
-
Hepatorenal syndrome
Track 6: Hepato-Cardiac and Pulmonary Disorders
Hepato-cardiac disorders are defined as the liver disease affecting the heart or the heart disease affecting the liver or the condition affecting heart and liver at the same time. During the Differential diagnosis of liver injury or disease, in a cardiologist, clinical practice, ask for collaboration between the hepatologists and cardiologists. In patients with the advanced liver disease may show and various abnormalities like some diastolic and systolic dysfunctions, reduced cardiac performance. Cardiac evaluation in liver disease patients is important, after a liver transplantation may improve cardiac function or have a reversal effect. Systemic disease with effect liver and heart are congenital, inflammatory and metabolic and alcoholism. The Hepato-pulmonary disorder which causes low oxygen levels in your blood is associated due to the formation of microscopic intrapulmonary arteriovenous dilations occurring in patients with liver cirrhosis. The mechanism is obscure due to increased hepatic production or decreased hepatic clearance of vasodilators. Due to the overperfusion related to ventilation, causes vascular dilations especially in increased cardiac yield individuals with resulting from systemic vasodilation and people having low oxygen levels in the blood encounter shortness of breath, which can become more severe over time.
-
Portal hypertension
-
The hepatopulmonary syndrome
-
Hepatic hydrothorax
Track 7: Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is the condition which occurs when normal cells in the liver become abnormal in appearance and destructive to the adjacent normal tissues, which can spread to other areas of liver or to the other organs outside of the liver. Cancer cells are characterized by the procurement of several capacities amid the stages of tumorigenesis, maintenance of proliferation signaling, induction of angiogenesis, activation of invasive resistance to cell death, inhibition of growth suppressors, and metastatic pathways, ability to evade immunological destruction and alteration of cellular metabolism. The clonogenic capacity of stem cells was evaluated by the stem cell colony formation assay.
-
Liver cell carcinoma
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
-
Hepatoma
-
Cholangiocarcinoma
-
Hepatoblastoma
-
Angiosarcoma of liver
-
Kupffer cell sarcoma
-
Other sarcomas of liver
Track 8: Neurology and Liver Disease
Neurological deficits related to liver illness may influence the CNS, the peripheral nervous framework, or both. The most serious neurological complication of acute liver failure and hepatic encephalopathy result in the advancement of the brain edema. Cognitive dysfunction is detected in Hepatitis C along with serious fatigue and mood disorders. Alterations in the brain metabolites show CNS change in these patients when recognized by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. The most widely recognized aspect of this relation is that hepatocellular failure may be complicated by the behavioral syndrome of hepatic encephalopathy, in which neurotransmission in the brain altered, profound fatigue in patients with chronic cholestasis is, may also be associated with altered neurotransmission in the brain.
-
HCV/HIV Co-infection epidemiology
-
Wilson Disease
Track 9: Hepatic Pathology
Histological examinations of liver biopsy before treatment showed accumulation of fat within the hepatocytes, bile duct endothelium and epithelium and kupffer cells which contain the portal macrophages. The liver serves as the filtration ground of absorbed intestinal luminal contents which are particularly susceptible to microbial antigens.
-
Transudative Ascites
-
Cholestasis
-
Centrilobular Necrosis
-
Peliosis hepatis
Track 10: Pediatric and Geriatric Hepatology
Liver diseases are mostly seen as in a grown-up, however, a huge number of children from babies to teens experience from different types of liver diseases. The volume of the liver and the blood flow decreases with age, immune responses against pathogens or neoplastic cells are lower in the elderly reducing their tolerability to treatments for liver diseases. Liver regeneration capacity shows a decline in age, reduced proliferation of hepatocytes, but the level of hepatic enzymes and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is well maintained. Pediatric hepatology focuses on the diagnosis and treatment of liver and liver-related disease in infants and children.
-
Gilbert’s disease
-
Hemochromatosis
-
Liver Failure
-
Liver Cirrhosis
-
Hepatorenal syndrome
-
Liver Fibrosis
-
Neonatal Jaundice
Track 11: Hepato-Biliary Diseases
Hepato-biliary diseases includes a heterogeneous group of liver and biliary system caused by bacterial, viral and parasitic infections, toxic chemicals, alcohol consumption, metabolic disorders, cardiac failure, and neoplasia. Some of the hepato-biliary diseases appear to be a genetically determined metabolic trait; the physiological abnormality underlying the formation of gallstones is an accumulation of bile supersaturated with cholesterol causing cholesterol gallstones. Recent progress in the molecular biology and genetic control of lipoproteins and lipids metabolism may provide an opportunity for new studies on these diseases.
-
Primary biliary cholangitis
-
Caroli disease
-
Bile duct hamartoma
Track 12: Hepatitis
Hepatitis occurs due to the inflammation in tissues of the liver caused due to the viral infection which can harm the organ which may further lead to cirrhosis, fibrosis and liver cancer. Hepatitis is a devastating disease that progress slowly but results in damage to the liver. Hepatitis A is the most common cause’s acute hepatitis in children in the Middle East. Establishment of HBV vaccination to cover all neonates and high-risk group, screening of donor blood can help in improving the case. Recent advancement in the treating hepatitis built on incremental improvements can transform it into new forthcoming treatments that can be potentially cured.
-
Autoimmune hepatitis
-
Alcoholic hepatitis
-
Viral Hepatitis
-
Granulomatous hepatitis
Track 13: Liver Disease and Pregnancy
Certain liver diseases are uniquely associated with pregnancy like Hyperemesis gravidarum is intractable, dehydrating vomiting in the first trimester of pregnancy occurs due to liver dysfunction. Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy is pruritus and elevated bile acids in the second half of pregnancy, accompanied by high levels of aminotransferases and mild jaundice. The common condition in hepatic tenderness and liver dysfunction in pregnancy is severe preeclampsia it is further complicated by low platelet count, elevated liver tests, and hemolysis. Signs and symptoms of liver disease during pregnancy is not specific, fertility can be restored by liver transplantation by this pregnancy may have a good outcome.
-
Hyperemesis gravidarum
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
-
HELLP syndrome
Track 14: Colorectal Disease: Treatments & Diagnosis
Colorectal Disease substantially varies from benign lesions to malignant and cancerous growth. Colorectal cancer is the 3rd leading cancer-related death; the main cause of death is liver metastasis which leads to a liver tumor. A variety of tests and procedures are used to screen and diagnose colorectal disease, including Colonoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, Endoscopic ultrasound, Capsule endoscopy.
-
Screening and therapeutic colonoscopy
-
Endoscopic ultrasound
-
Endoscopic mucosal resection
-
Anal manometry
-
Colorectal cancer surgery( proctology)
-
Fecal microbiota transplant
-
Pelvic floor physical therapy
Track 15: Liver Transplantation and Surgery
Liver transplant is an operation that replaces a replaces a person’s diseased heart with a partial or a whole liver from a donor. A rare condition in newborn infants is Biliary atresia in which the common bile ducts, which carry bile out of liver and present between the liver and small intestine is absent or blocked. Bariatric surgery performed on people, who have obesity through a variety of procedures. Removing a tissue sample (biopsy) from the liver may help diagnose liver disease. Liver biopsy is done using a long needle inserted through the skin to extract a tissue sample and then analyzed in a laboratory.
-
Immunosuppressive management
-
Graft rejection
-
Living donor transplantation
-
Bariatric surgery
-
Liver Biopsy
Track 16: Liver Imaging Modalities
Liver imaging is basically for precise diagnosing biliary tract issue and is imperative for identifying liver injuries or damage and patients with a suspected malignancy is important because the liver is the common site of metastatic spread and those who are at the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma.
-
Ultrasonography
-
Computerized Tomography
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
-
Angiography
-
Positron Emission Tomography
Scope and Importance:
Liver Congress 2018 have invited worldwide experts on Hepatology, cardiology, neurology, Gastroenterology, and Endoscopy, they will give lectures and will demonstrate the latest developments in Hepatology in complementarity with cardiology, neurology, obesity, Gastroenterology & Pregnancy, Hepatitis & Liver Diseases, microbiology during the presentations. New scopes will be shown as new accessories.
Hepatology is a sub-specialty of gastroenterology that incorporates the study of Liver, biliary tree, gallbladder, and pancreas as well as management of disease and disorders associated with them. Some of the cases associated with Liver include Jaundice, Liver Cancer, Liver Transplantation, drug overdose, biliary infection bleeding, pancreatitis, GIT bleeding, etc. Although there is a reduction in deaths due to gallstone disease and gallbladder cancer, liver-related mortality has remained relatively stable over the last 30 years. Hepatology represents a growing problem for the international healthcare systems and first of all, for the patients.
Why Abu Dhabi?
Nearly 30 percent of the UAE’s adult population could be suffering from non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, a condition that is closely linked to diabetes and metabolic syndrome, medical professionals have warned. And without proper care, the disease could significantly increase the risk of developing cardiovascular complications and liver damage. About 51 Emirati patients have so far undergone living donor liver transplants at our facility, and they make up the largest ethnic group among our patients. About 43% of all Emirati patients who had liver cancer had undergone liver transplantation and 32% have been suffering from liver damage from hepatitis B and C. In fact, most ultrasounds do not pick up on fatty livers unless 30 percent of the organ’s mass is made up of fat. And it is likely that prevalence rates in the UAE are similar to the United States’ prevalence of 20 to 30 percent of the adult population.
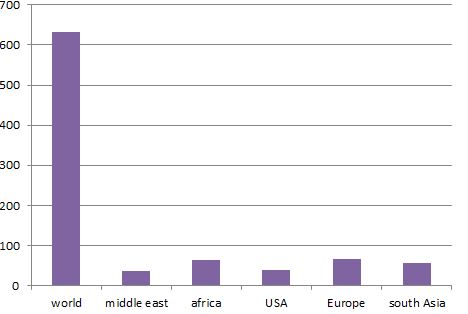
The above graph represents the number of death of people with liver cancer and various liver diseases in comparison to the world and among the continents.
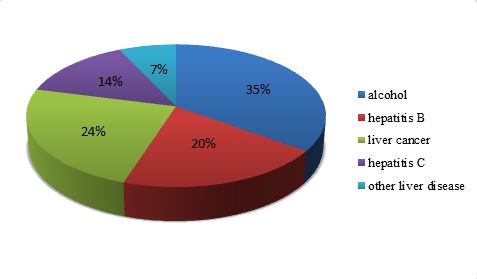
Most of the liver death results due to the alcohol consumption, viral hepatitis and various types of liver cancers. The above graph represents people mortality rate in reference to alcohol consumption, liver cancer, hepatitis and other liver diseases.
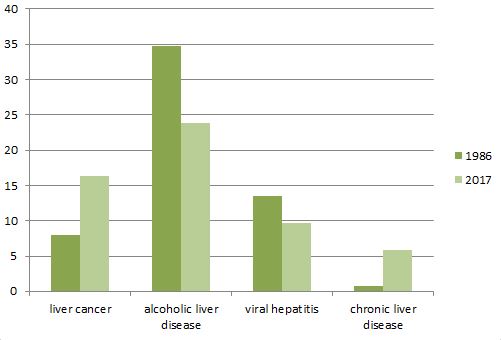
In the above graph, represents the number of death per individual has been reduced in few decades, the number death per 100,000 people in the year 1986 and 2017 were plotted, with the development in the field of research and advancement in liver hepatology have reduced the annual deaths.
Great progress has been made in the field of liver transplantation over the decades, however, the progress has brought up quite a few challenges like shortage of organs and organ donors and large proportion waiting list of patients. There has been a significant effort in the improving the number of the donor pool. With the improvement in the understanding the pathophysiology of liver allograft, conditions, like the cardiac arrest various factors can be improved which will in turn help in the development of mechanical perfusion strategies. Long-term results of liver transplant recipients have not improved significantly, as recipients continue to succumb to complications of long-term immunosuppression, such as contamination, malignancy, and renal failure. Furthermore, recent evidence suggests that unremitting immune-mediated injury to the liver may also affect graft function.
Evolution of HCV Therapy:
In the United States, 20 percent to 30 percent of individuals living with HIV are co-infected with HCV. Hepatitis C is common among individuals living with HIV. This implies that approximately 225,000 to 330,000 individuals in the United States are living with both viruses. The larger part of individuals living with hepatitis C does not know they have it. The most common course of transmission in the UK is utilizing non-sterile needles and other equipment for infusing drugs. 90 percent of individuals who got HIV from infusing drugs are moreover infected with HCV. This is since both infections can be spread effectively through blood and blood products.
Major societies and Associations related to Liver
Middle East
Israel Gastroenterology Association
Egyptian Liver Foundation
Liver Transplantation Society
Saudi Center for Organ Transplantation
Turkish Transplantation Centers Coordination Association
The Transplantation Society- Turkey
Kuwait Transplant Society - Rawda
The Lebanese Society of Gastroenterology
Yemeni Study Association for Liver, Biliary, GIT diseases
Egyptian Society of Endoscopy and Hepatogastroenterology
Cyprus Society of Gastroenterology
Palestinian Society of Gastroenterology
Hepatitis B and C Public Policy Association
Jordan Cancer Society
Jordanian Society of Gastroenterology
The Syrian American Medical Society (SAMS)
Mikati Foundation Hepatopancreaticobiliary and Liver Transplantation Unit
Potamitis Gastroenterology & Nutrition
Saudi Gastroenterology Association
Emirates Gastroenterology & Hepatology Society
Yemen Gastroenterological Association
Turkish Society of Gastroenterology
The Israeli Society of Gastroenterology and Liver Disease
Iraqi Society of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Iranian Association of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Asia-Pacific
Australasian Hepatology Association
Chinese Society of Gastroenterology
Gastroenterological Society of Australia
Gastroenterological Society of Singapore
The Gastroenterological Association of Thailand
Hepatology Society of the Philippines (HSP)
Indian National Association for Study of the Liver (INASL)
Indonesian Association for the Study of the Liver
South Asian Association for the Study of the Liver
The Japan Society of Hepatology
The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver [APASL]
Hepatology Society of the Philippines
The Coalition to Eradicate Viral Hepatitis in the Asia Pacific
The Hong Kong Association for the Study of Liver Diseases
Pakistan Society for the Study of Liver Diseases (PSSLD)
Asian Pacific Association of Gastroenterology (APAGE)
The Hong Kong Society of Gastroenterology
The Indian Society of Gastroenterology (ISG)
The Gastroenterological Association of Thailand (GAT)
Gastroenterological Society of Taiwan
Gastroenterological Society of Singapore
Philippine Society of Gastroenterology
The Pakistan Society of Gastroenterology and GI Endoscopy
Malaysian Society of Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Myanmar Gastroenterology and Liver Society
The Korean Society of Gastroenterology
Japan Gastroenterology Society General Foundation
Bangladesh Gastroenterology Society
Center for Disease Analysis Foundation
Asian Institute of Gastroenterology
Chennai Liver Foundation (CLF)
Hong Kong Liver Cancer and Gastrointestinal Cancer
The USA- Europe
Alabama Gastroenterological Society
San Diego Gastroenterology Society
Southern California Society of Gastroenterology
American College of Gastroenterology
The Louisiana Gastroenterology Society (LAGIS)
Mississippi Gastroenterology Society
New Jersey Gastroenterology & Endoscopy Society.
New York Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy
North Carolina Society of Gastroenterology - NCSG
The Ohio Gastroenterology Society
Pennsylvania Society of Gastroenterology
Virginia Gastroenterological Society
The Ontario Association of Gastroenterology (OAG)
The British Association for the Study of the Liver
International Liver Cancer Association (ILCA)
European Liver Patients Association
Kidney and Liver Association
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases
Swedish Gastroenterological Association
The Swiss Society for Gastroenterology
British Society of Gastroenterology
Austrian Society of Gastroenterology and Hepatology
House of European Gastroenterology
Ukrainian Gastroenterology Association
Finnish Gastroenterology Association
Bulgarian Society of Gastroenterology
Secretariat of the Czech Gastroenterological Society
Italian Society of Gastroenterology and Digestive Endoscopy
Lithuanian Society of Gastroenterology
PHI University Clinic for Gastroenterohepatology
Association of gastroenterohepatologists of Montenegro
Dutch Society for Gastroenterology
Norwegian Gastroenterological Society
Flemish Association for Gastroenterology
Croatian Gastroenterology Society
Polskie Towarzystwo Gastroenterologii
Sociedade Portuguesa de Gastrenterologia
Hellenic Gastroenterological Society
Irish Society of Gastroenterology
Romanian Society of Gastroenterology
Russian Gastroenterological Association
Slovak Gastroenterological Society, oz
Slovenian Association for Gastroenterology and Hepatology
Spanish Association of Gastroenterology
Hungarian Gastroenterological Society
Association of Serbian Gastroenterologists
Gastroenterological Scientific Society of Russia
Related Conferences
1. 16th International Conference on Gastroenterology and Digestive Disorder, August 06-07, 2018 Abu Dhabi, UAE
2. 17th International Conference on Gastroenterology and Hepatology, September 03-04, 2018 Dubai, UAE
3. International Metabolic Diseases and Liver Cancer Conference, September 17-18, 2018 Dubai, UAE
4. 6th World Congress on Hepatitis & Liver Diseases, June 18-20, 2018 Dublin, Ireland
5. Euro Global Congress on HCV, June 28-30, 2018 Amsterdam, Netherlands
6. 15th International Conference on Digestive Disorders and Gastroenterology, July 11-12, 2018 Sydney, Australia
7. 14th Annual Congress on Gastroenterology & Hepatology, August 6-7, 2018 Osaka, Japan
8. 13th Euro-Global Gastroenterology Conference, August 20-21, 2018 Rome, Italy
9. 14th International Conference on Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, August 29-30, 2018 Toronto, Ontario, Canada
10. 18th World Gastroenterologists Summit, September 7-8, 2018 Auckland, New Zealand
11. 3rd International Conference on Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Disorder, September 17-18, 2018, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA
12. 3rd International Conference on Digestive and Metabolic Diseases, Oct 22-23, 2018, Berlin, Germany
13. 4th World Congress on Digestive & Metabolic Diseases, October 29-30, 2018, San Francisco, California, USA
14. World Summit on Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatitis, November 07-08, 2018 Singapore
15. 15th World Congress on Gastroenterology & Therapeutics, November 08-09, 2018 Auckland, New Zealand
16. World Gastroenterology & Hepatology Conference, September 10 - 12, 2018, Rome, Italy
17. International Conference on Gastroenterology, Dublin, Ireland, June 25-26, 2018
18. 8th Annual Gastroenterology and Hepatology Symposium, February 15-16, 2019, Florida
Can Food-derived antioxidants halt or prevent fatty liver disease?
As there is an increase in obesity in the world, non-alcoholic liver disease (NAFLD) has become a major health issue, in turn, increasing liver transplants and cancer. The non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is characterized by excessive lipid accumulation in hepatocytes which further leads to various liver disease. There are many anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidants, insulin sensitizer dietary supplements which show beneficial effects on NAFLD.
An anti-oxidant found in papaya, celery, parsley and in kiwi fruit called pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) which can halt or prevent the progression of fatty liver. Most childhood obesity and fatty liver disease are influenced by the infant’s microbiome and maternal diet. According to the results, the significance of the neonatal period is an important window to protect obese offspring from the ill effects of diet-induced lipotoxicity and potentially halt the increasing NAFLD associated with childhood obesity.
Overconsumption of high-fructose corn syrup in soda and fat forming, pro-inflammatory effects which appear in the transient ATP stage can lead to the formation of uric acid. The normal level of uric acid acts as anti-oxidants but the high level can harm the cells and also associated with the increased risk of developing high blood pressure, diabetes, kidney disease and obesity.
Prevention:
Fructose: similar to alcohol can damage our body and liver
Eating right and exercising can prevent this condition and reverse at its early stage.
Development of a xenograft model zebrafish to study the liver cancer cell lines
Most occurring disease in the liver is Hepatocellular carcinoma which affects nearly a million every year, affects in people having Hepatitis B and C infection which is also associated with the cirrhosis mainly caused due to exposure of aflatoxin B, chronic alcohol use. Liver cancer patients show the difference in prognosis, so it's important to discover the target genes and ACHE Acetylcholinesterase is the target gene, any change in the amount of ACHE is associated with cancer prognosis and can be degraded by the enzymatic action of acetylcholine. Recombinant ACHE treatment decreases cell proliferation in liver cancer cell lines expressing themselves in mice xenograft model decreases tumor size.
Xenograft models for liver cancer have been developed in different organisms; use of multiple tumor cells has been proposed to observe different tumor phenotypes. Having a hundred transparent offspring enabling ease of imaging and lack of early developmental adaptive immune system, made them emerge as a model for tumor xenotransplantation studies.
Alcohol-induced bone marrow damage or Bone marrow Suppression from Alcohol abuse
Bone marrow is responsible for producing white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. A direct result of alcohol abuse is to the liver, brain, and heart but apart from that, it results in low platelets, anemia, and leukopenia. WBC provides resistance to infections and RBC is vital for transporting oxygen and energy. Excessive drinking cause’s destruction of WBC and RBC and platelets, as it interferes with the production of the cells making the person weak, tired and vulnerable to the infection.
Bone marrow suppression results in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria known as blood in the urine and Myelodysplastic Syndrome which is characterized by mutated cells, Alcoholism is the leading cause of thrombocytopenia. Alcohol adversely affects osteoblast activity, suppressing new bone formation needed in both normal bone remodeling and fracture healing, Studies show that bone-marrow biopsy samples from alcoholics are abnormal approximately two-thirds reveal sideroblastic and or megaloblastic changes and fewer shows iron deficiency and the marked hemolysis of spur cell anemia found in patients with jaundice and severe alcoholic cirrhosis. Generalized reduction in blood cell numbers is not progressive or fatal and is reversible with abstinence, complex aberrations of hematopoiesis can develop over time which may cause death.
Gut Health Issues — Microbiome and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
The microbiome in our body is made of 100 trillion bacteria which lines the gut. These type of bacteria that flourish or perish have a substantial impact on our health and liver health.
Study based on obese people found that microbiome had a reduced type of bacteria called Bacteroidetes and an abundance of another bacteria called Firmicutes. This ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes lead to an increase in lipopolysaccharide absorption.
Lipopolysaccharides are a component of the cellular membrane of gram-negative bacteria like Bacteroidetes. Endotoxins like Lipopolysaccharides that trigger an inflammatory response in the body which contributes directly to the resistance of insulin in the liver and obesity.
The microbiome is unique in every human being it differs due to the diet. Based on the type of diet reduces the diversity of the microbiome, favoring an increase in the Firmicutes-to-Bacteroidetes ratio in the gut. As a result, causing obesity-microbiota profile that favors the development of obesity and fatty liver disease. As the lipopolysaccharide absorption increases, due to the poor diet and increase of microbiome destabilizes the liver function and non-alcoholic liver disease progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Dermatological Manifestation of Gastrointestinal Disease
The liver is the metabolic production line of the body which produces energy to maintain functions performed in the body cells. The hair follicles require the energy to develop strong shiny hair and skin cells require vitality to eliminate toxins and regenerate and repair themselves. In the event that the liver does not work appropriately, the toxins would not be broken down and would be eliminated through other means like skin cells.
The excessive toxins would be deposited in the deep layers of skin causing inflammation and can give the ride to different disease like
• Eczema
• Dermatitis
• Psoriasis
• Acne and Acne rosacea (small pimples on face)
• Red itchy rashes on the body
• Wrinkling of skin and premature aging
• Brown liver spots
• Hives
There are different kinds of skin related problems, using conventional methods can suppress it, but comes with side effects, look for a deeper cause which is usually the liver and treat it with nutritional medicines.
A major variety of skin problems can be treated through various natural approaches:
• The liver needs high requirement of antioxidants which is found in vegetables mostly green leafy and these antioxidants help in protecting liver cells from damage by detoxifying the bloodstreams, removing free radicals from skin cells which causes premature aging.
• Omega 3 supplements present in fish oil helps in preventing chronic skin problems.
• Selenium: a mineral that exerts anti-inflammatory effects in the body and is used for the production of glutathione which is an antioxidant.
Other liver-related problems:
Jaundice: The symptoms of skin and the whites of the eyes look yellowish is due the to break down a chemical called bilirubin which builds up in the blood, and makes the skin turn yellow. It is the sign of infection with hepatitis C.
Itching: The toxins that build up in the blood and because jaundice can also cause itching in hands and legs sometimes in the organs also.
Liver Toxicity and Drug Allergy
The liver main function is to purify blood by filtering out the toxins so that the body can absorb healthy nutrients that remain. Some drugs are directly injurious to the liver, other are transformed into chemicals by the liver.
Three types of toxicity
· Dose-dependent toxicity-
· Idiosyncratic toxicity
· Drug allergy
Drugs that cause dose-dependent toxicity can cause liver malady in most individuals in case sufficient of the medication is taken.
Drugs that cause idiosyncratic toxicity cause disease in few patients who have inherited specific genes that control the chemical transformation of that specific drug by the accumulation of the drug or products of their metabolites that are harmful to the liver. The Inherited idiosyncratic toxicities are rare and depend on the drug. The idiosyncratic liver disease is the most common form of the drug-induced liver disease even though the risk of developing the drug-induced idiosyncratic liver disease is low.
Drug allergy is the most uncommon form of liver disease. There is inflammation of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system is attacked by the drugs with antibodies and immune cells.
Many drugs cause mild elevations in blood levels of liver enzymes without showing any symptoms or signs of hepatitis. AST, ALT, and alkaline phosphatase are enzymes that usually reside within the Hepatocytes and bile ducts and can cause the enzymes to leak from the liver cells into the blood, in a way elevating the blood levels of the enzymes.
The neurological manifestation of Acute Liver Failure
When the liver is damaged, the toxins or the poisons can build up in the bloodstream and influence the brain function and the nervous system. Acute liver failure leads to the critical condition is known as brain swelling and as a rule, causes death in patients who suffer from this complication. Preventing brain swelling and optimizing brain perfusion when brain swelling occurs it may be a critical component in making the option of good survivorship in patients with acute liver failure. Conventional approaches are made to limit the brain swelling and lowering intracranial pressure (ICP) which is not reliable in patients with ALF. While observing ICP is a critical step toward appropriately treating these patients, the ALF causes a coagulopathy that often creates hesitance for inserting an intrusive device into the cranium. An efficiently considered is done to approach, present and distributed comes about of demonstrating the safe insertion of ICP monitors in ALF patients without causing any noteworthy hemorrhagic complications. It is an important step toward changing the clinical approach to optimize brain perfusion and neurological outcome in ALF patients.
A strong interest is developed in the role of continuous hemodialysis techniques to facilitate ammonia clearance, and we have a project dedicated to correlate dialysis flow rates to the quality of ammonia clearance. The mechanism of brain swelling from ALF relates to hyperammonemia. The liver produces urea from ammonia as a by-product of protein metabolism. When there is an acute liver failure, the ammonia accumulates and is an important contributing factor to the development of brain swelling. The elevated level of ammonia in the astrocytes also known as brain cells is enhanced due to the conversion of glutamic acid to glutamine and this leads to cellular swelling further aggregate to brain swelling. High ammonia concentrations may have some toxic effects on neurons in addition to its role in astrocytic swelling.
Cancer cells adapt to gorge on sugar within the liver
The Metastatic cancer cells can reprogram their metabolism to flourish in new organs. The finding shows that the colorectal cancer cells originating have changed their dietary habits to capitalize on the high levels of fructose often found in the liver. Cancer becomes much more deadly when it spreads to different parts of the body. In the study, it is found that certain metabolic genes became more active in liver metastases than they were in the original primary tumor or lung metastases. One group of metabolic genes was unique which are involved in the metabolism of fructose which in turn made the researchers think as because many Western diets are rich in fructose, which is mostly found all types of processed foods and in corn syrup.
When cancer cells are is proliferated into the liver, they use this ample new energy supply to create building blocks for growing more cancer cells. So they feed on fructose, which further makes the cancer cells to produce more of an enzyme which breaks down fructose, called ALDOB, which mostly done in the liver. The proliferation of cancer cells is quickened and become unstoppable, once they figure out how to adapt themselves to thrive on fructose. Besides providing an insight into how cancers thrive after metastasizing, this discovery can lead to new therapies specifically targeting metastatic cells. The fructose metabolism cannot be blocked but can be halt by avoiding fructose-containing non-processed foods, and by eating natural and providing drugs that block fructose metabolism. New drugs targeting fructose metabolism have recently been developed by pharmaceutical companies to treat the metabolic diseases.
Obesity May Impact Liver Health of Young Children
Obesity is the fastest emerging concern in the nation circuit and global health. According to the latest study it is found that there may be a negative impact on the liver health in children, may also accumulate fats in the liver by causing serious liver disease. Too much of fat accumulation in the liver may cause non-alcoholic liver disease which may progress to cirrhosis and later liver cancer.
NAFL is normally symptomless. Elevated ALT, the liver enzyme in the measured blood levels occurs in the person having the Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Children with bigger waist circumference also known as the measure of abdominal obesity are more likely have elevated ALT.
Measures:
One of the perfect ways for kids and adults to combat fatty liver disease is to lose weight the healthy way. Staying away from fried and processed foods, maintaining a strategic distance from sugary beverages and products, is additionally a must to manage weight better. Swap refined carb sources for whole grains. A whole grain could be a grain of any cereal that contains the endosperm, germ, and bran, in contrast to refined grains, which hold only the endosperm. A whole grain holds all the supplements that are processed within the refining. Stock up on whole grains like bajra, ragi, maize and jowar and utilize them frequently. Stack up on regular vegetables. They give both soluble and insoluble filaments in addition to vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which are exceptionally essential for a perfect state of health.
Gastric Drugs may heighten the risk of liver diseases
Proton Pump Inhibitors are drugs that can reduce the gastric acid, but can promote the growth of a type of bacteria which is associated with a chronic liver disease. These PPl are used to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease which produces an uncomfortable burning sensation when travels up the esophagus.
Our stomach produces gastric acid to inhibit the ingested microbes and taking medication to suppress gastric acid can change the microbiome of the liver. An absence of gastric acid can promote the growth of Enterococcus bacteria which primarily lives in the intestine then translocate to the liver, where the cause of inflammation and chronic liver diseases.
The effect of gastric acid suppression promotes a series of liver diseases
Alcoholic liver disease
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
E-Cigarettes may contribute to the accumulation of the fat in the Liver
The Electronic cigarettes have been quickly increasing, since that, they are more secure than conventional cigarettes as the reason that the additional fat within the liver is likely to be hindering to health, which therefore concludes that e-cigarettes are not as safe as they have been advanced to consumers. E-cigarettes contain nicotine; in any case, the long-term impacts of e-cigarettes on, diabetes, heart disease, liver illness or stroke are unknown.
According to the 12-week study, may a study in the mice missing the gene for apolipoprotein E, which makes them more prone to developing heart disease and fat in the liver. All of the mice were fed a diet which is relatively high in fat and cholesterol. One group of mice was put in a chamber that exposed them to e-cigarette aerosol so that their blood nicotine levels were similar to that of smokers and e-cigarette users. The second group of mice was exposed to the saline aerosol.
The researchers collected the liver samples and there were examined the genes in the liver affected by e-cigarettes using a technique called RNA sequence analysis. There was an alternation in 433 genes that were associated with the fatty liver development and in progression for the mice when exposed to e-cigarettes. The researchers also found that genes related to circadian rhythms (the body clock) were changed in mice exposed to e-cigarettes. Circadian rhythm dysfunction is also known to accelerate the development of liver disease including fatty liver diseases.
Can Aspirin a day keep liver cancer away?
The researchers found that everyday aspirin therapy might result in a lower hazard of hepatitis B related liver cancer, could be a viral disease that affects the liver. HBV can be contracted through contact with a contaminated person’s blood or other substantial liquids, and the infection can either be acute or chronic. Aspirin has been studied to investigate its chemo-preventive impact in cancers that are related to persistent inflammation, particularly in the prevention of colorectal cancer. In some cases, clinical supporting the chemo-preventive impact of aspirin treatment on liver cancer remains restricted. Therefore, they have conducted a largeâ€scale study to evaluate the affiliation of aspirin therapy with HBVâ€related liver cancer.
Cumulative frequency of liver cancer treated with headache medicine treatment was found essentially lower than that of the untreated group in five years. In their multivariate regression examination, the researchers found aspirin treatment was autonomously associated with reduced liver cancer chance. Sensitivity subgroup analyses too confirmed this association. Older age, male sex, cirrhosis, and diabetes as well were independently related with an increased hazard, but nucleotide analogue or statin use was related to a decreased risk. For effective prevention of HBVâ€related liver cancer, the discoveries on this study may offer further assistance to the Hepatologists in treating the patients having chronic HBV infection in the future, who is not demonstrated for antiviral therapy especially. They are further pursuing arranged examinations for advance confirming the discoveries.
Black seed oil is the latest ‘cure-all’ wellness ingredient
Wellness is at the forefront of everybody’s minds, and whether you select to taste on a turmeric latte or you’ve supplied upon actuated charcoal, more of us than ever are turning to a characteristic approach for our wellbeing. Presently a modern superfood is trending within the prosperity world, with specialists claiming that it can soothe hypersensitivities, relieve dermatitis, help digestion and support the immune system.
Believed to be Cleopatra's beauty secret, Black Cumin also known as Nigella sativa is discovered to have anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, anticancer, and immune-enhancing properties, also an abundant source of all the essential fatty acids, proteins and vitamins B1, B2,B3, calcium, folate, iron, copper, zinc and phosphorus, as well as the antioxidants thymoquinone, carvacrol, thymol, p-cymene, anethole, and 4-terpineol – which provide strong anti-pathogenic and antifungal properties. Black oil seed can help treat functional liver diseases and also improves liver function and prevention of liver damage, liver disease, as well as type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Some studies on this potent seed oil show it may also be helpful in combating superbugs like MRSA or h.pylori.
Pure dark seed oil comes in the form of a dull fluid which can be ingested orally – one teaspoon per day – and it incorporates a slightly biting taste that won’t be for everybody. There are magnificence benefits as well. Because of its solid antioxidant properties, black seed oil in an entirety has of topical items outlined to feed the dry skin and clear blemishes.
Kiwi compound may prevent non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
There is increasing evidence that we are what moms ate amid pregnancy; in case they consumed a high-fat count calorie, at that point we might suffer the consequences, be it weight or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A modern study, however, may have uncovered a way to avoid the latter. Researchers found that a compound called pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) which is found in celery, kiwi, and papaya which in turn prevents the movement of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mice who were nourished a high-fat diet. NAFLD is characterized as a buildup of fat within the liver that's not caused by alcohol consumption. It is estimated that NAFLD influences adults, making it one of the foremost common causes of liver disease. Hypertension, obesity, high cholesterol levels, and high triglyceride levels are key factors to NAFLD, and these conditions also lead as a result of a high-fat diet.
But it's not fair the nourishment that we got to be concerned almost; the wellbeing may well be the chance as a result of the nourishment that mother had at their amid pregnancy. An overpowering number of considers has shown that the maternal count calories can take off a negative mark on the developing infant. Research has also shown that destitute maternal count calories may alter the intestine microbes of offspring in a way that makes them inclined to corpulence and related conditions. This leads to long-lasting postnatal disturbances of the offspring's natural resistant system and guts bacterial health, which may increment the chance for improvement of fatty liver disease.
PQQ is a compound present in plant-based foods like green peppers, kiwi, celery, parsley, and papaya and human breast drain, which implies offer assistance to protect our body against free radicals, which are uncharged molecules that can damage DNA and other cellular components. This also determines whether maternal PQQ supplementation might offer assistance to anticipate the advancement of NAFLD in offspring. To reach their discoveries, the researchers encouraged pregnant mice a high-fat.
Mice, nourished with the high-fat count calories, develop a change in gut microbes which were associated with the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a form of NAFLD in which fat build-up within the liver is going with by inflammation. When mice who were treated with PQQ alongside their high-fat diets, the researchers found that the NASH-associated gut microscopic organisms changes in their offspring were reversed, and they too appeared less weight pick up than sibling that did not get PQQ. Although levels in incline versus obese mothers have not been examined in humans or animals, PQQ could be a possibly secure helpful to test for the avoidance of developmental programming of NAFLD/NASH.
Symptoms of a Cyst on the Liver
Non-parasitic hepatic cysts are benign entities, occur within the liver in the majority of cases, and are asymptomatic. Cysts can cause indications when they ended up large and produce bile duct compression or portal hypertension, conjointly when complications such as burst, contamination or hemorrhage take place. A liver cyst could be a fluid-filled sac that develops along the liver, the largest organ within the human body. Whether an individual develops symptoms of a liver cyst regularly depends upon the size of the cyst; large liver cysts can cause symptoms, whereas smaller liver cysts generally do not.
Because a small liver cyst doesn’t more often than not show indications, it can go undiagnosed for a long time. It isn’t until the cyst enlarges that a few individuals experience pain and other inconvenience. As the cyst gets to be bigger, symptoms might include stomach bloating or pain within the upper right area of the stomach. In case you experience significant enlargement, you might be able to feel the cyst from the outside of your stomach. Sharp and sudden pain within the upper area of the stomach can happen in case the sore starts to bleed. In some cases, bleeding stops on its claim without restorative treatment. In the event that so, pain and other indications may progress within one or two of days.
Liver cysts are the result of a malformation within the bile ducts, in spite of the fact that the precise cause of this malformation is unknown. Bile may be a fluid made by the liver, which helps in digestion. This fluid travels from the liver to the gallbladder through channels or tube-like structures. A few individuals are born with liver cysts, while others don’t develop cysts until they’re much older. When the cysts are present at birth, they might go undetected until the indication occurs afterward in the adulthood.
There is a link between liver cysts and a parasite called Echinococcus which is a parasite found in areas where cattle and sheep in habitat. The contaminated in the case when ingesting sullied food. The parasite can cause the development of cysts in the liver and also in various parts of the body. Within the case of PLD, this illness can be acquired when there’s a family history of the condition, or the infection may happen for no clear reason. Cysts may bleed intensely, causing intense pain and begin to influence liver function. In these circumstances, the specialist may suggest a liver transplant.
How to Use Beets to Benefit the Liver?
Liver health might not be the primary thing that comes to intellect when we think around making a more advantageous way of life choices. The as it were the organ that influences numerous other aspects of our wellbeing extending from blood, stomach related, heart, and adrenal wellbeing. The liver is capable of detoxification, getting freed of harmful wastes and filtering out what it doesn’t require before it discharges blood back into the bloodstream. Everything that enters the mouth eventually closes up within the digestive system and within the blood. The bodies break down nourishment into cellular fuel for the blood so the supplements within the nourishment can lookout within the way nature planning. Man-made nourishments moreover hurt the well-being over time, especially within the liver due to the way it should process and channel. It especially channels chemicals, refined sugar, difficult to digest ingredients or alcohol. Beets contain an array of supplements that make them particularly useful for detoxification organs within the body. This incorporates the liver, stomach related system, and kidneys. Beets fortify lymphatic stream, they help in increase oxygen level by cleansing the blood, and they contain help with cleansing in every way. For your liver, beets are utilized to break down toxic wastes to help excrete them from the body faster. They do this by improving enzymatic action and stimulating bile stream. Beets are too a terrific source of fiber and Vitamin C, which naturally cleanses the digestive system.
Hepatology 2017
With the support of organizing committee Hepatology 2017 4th International Conference on Hepatology at Hotel J W Marriott in Dubai, UAE during April 27-28, 2017. The conference was designed around the theme of “To create global awareness and to share novel approaches on treating Liver and Pancreatic Diseases” and was a great success where eminent keynote speakers from various reputed companies made their resplendent presence and addressed the gathering. Moreover, the networking sessions laid the foundation for some time worthy collaborations between many start-up and big industries. The post-conference networking lunch session witnessed a number of B2B meetings that are turning up to be mutually beneficial to both the organizations who had gone in for the business meetings.
Hepatology 2017 witnessed an amalgamation of peerless speakers who enlightened the crowd with their knowledge and confabulated on various new-fangled topics related to the field of Gastroenterology and Hepatology. This congress not only brought forward the latest developments in the field but also provided solutions to the numerous challenges encountered in developing Hepatology field.
Our organization would like to convey a warm gratitude to all the Honourable guests, Keynote Speakers, Delegates, Media Partners and Exhibitors for their participation in Hepatology 2017.
Keynote Speeches:
Vomiting of Surgical Significance
- Amin El-Gohary, Burjeel Hospital, UAE
Total mesopancreas excision for pancreatic head cancer: analysis of 120 cases
- Ying Bin Liu, Xinhua Hospital, China
Management of NAFLD in patients with DMT2
- Hendrick Reynaert, Vrije University, Belgium
Renal involvement in patients with hepatitis B
- Yuming Wang, Southwest Hospital, Third Military Medical University, China
Surgery of the Liver and intraoperative interventional Therapies What is possible today?
- Hani Oweira, Hirslanden Hospital, Switzerland
Microscopic hepatico biliary anastomosis in staged adult living liver transplant is a safe and
accessible choice
- Ali Ghannam, CGMH Kaohsiung, Taiwan
Speakers:
Maridi Aerts, University Hospital in Brussels, Belgium
Ahmed S. Ibraheem, Sohag University, Egypt
Abdel Rahman Abdulla Al Manasra, Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan
Abdulaziz Shaher, Assir Central Hospital, Saudi Arabia
Mohammad Firoz Alam, Jazan University, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia
Reju George Thomas, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, South Korea
Hossien Kargar, Jahrom University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Rehan Saif, Aster DM Healthcare Group, India
Best Poster Award:
Alexander Hann, Katharinen hospital, Stuttgart, Germany
Naglaa Raafat, Dubai Medical College for Girls, UAE
We are also obliged to various delegate experts, company representatives and other eminent personalities who supported the conference by facilitating active discussion forums. We sincerely thank the Organizing Committee Members for their gracious presence, support and assistance towards the success of Hepatology 2017. With the unique feedbacks from the conference, 3rd World Liver Congress to be held on October 15-16,2018 at Abu Dhabi and also invite you to participate at our Liver Congress 2018.
Let us meet again @ Liver Congress 2018
Top medical universities in Europe
Wrocław Medical University
Brighton and Sussex Medical School
King's College London GKT School of Medical Education
Medical University of Silesia
School of Medicine, University of Zagreb
School of Clinical Medicine, University of Cambridge
Sheffield Medical School
Peninsula College of Medicine and Dentistry
Swansea University Medical School
Imperial College School of Medicine
Hull York Medical School
University of Birmingham Medical School
Leicester Medical School
Leeds School of Medicine
Southampton Medical School
Southampton Medical School
Bogomolets National Medical University
University of St Andrews School of Medicine
Top Medical Universities in USA
Harvard Medical School
Perelman School of Medicine
David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
University of California, San Francisco
Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine
Baylor College of Medicine
Pritzker School of Medicine
Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons
Boston University School of Medicine
Alpert Medical School
Top Universities In Asia
National University of Singapore (NUS)
Kyoto University
University of Hong Kong (HKU)
Peking University
Seoul National University (SNU)
National Taiwan University (NTU)
Osaka University
Tsinghua University
The Chinese University of Hong Kong (CUHK)
Fudan University
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST)
Taipei Medical University
Mahidol University
KAIST - Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology
Yonsei University
Shanghai Jiao Tong University
Nanyang Technological University (NTU)
Chulalongkorn University
Tohoku University
Tokyo Medical and Dental University
Kyushu University
Nagoya University
Hokkaido University
Sungkyunkwan University
University of Science and Technology of China
Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH)
Korea University
Top Medical Universities in Middle East
|
American University of Sharjah University of Jordan Jordan University of Science and Technology King Abdulaziz University Khalifa Unive rsity Qatar University American University of Beirut Alfaisal University King Saud University Beni-Suef University American University in Cairo Suez Canal University Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal University University of Tunis El Manar Sidi Mohamed Ben Abdellah University University of Monastir Sultan Qaboos University University of Marrakech Cadi Ayyad Mohammed V University of Rabat Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland – Bahrain Mohammed bin Rashid University of Medicine and Health Sciences Gulf Medical University, Ajman Dubai Medical College for Girls Gulf Medical University Ajman United Arab Emirates University Ras al-Khaimah Medical and Health Sciences University University of Sharjah |
Conference Highlights
- Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology & Hepatology
- Liver Inflammation and Immunology
- Liver Regeneration
- Gene Expression in Liver
- Hepato-Nephrology
- Hepato-Cardiac and Pulmonary Disorders
- Liver Cancer
- Neurology and Liver Disease
- Hepatic Pathology
- Pediatric and Geriatric Hepatology
- Hepato-Biliary Diseases
- Hepatitis
- Liver Disease and Pregnancy
- Liver Transplantation and Surgery
- Liver Imaging Modalities
- Colorectal Disease: Treatments & Diagnosis
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | December 17-18, 2018 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | Day 2 | |
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Liver
- Journal of Gastrointestinal & Digestive System
- Journal of Hepatology and Gastrointestinal disorders
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by